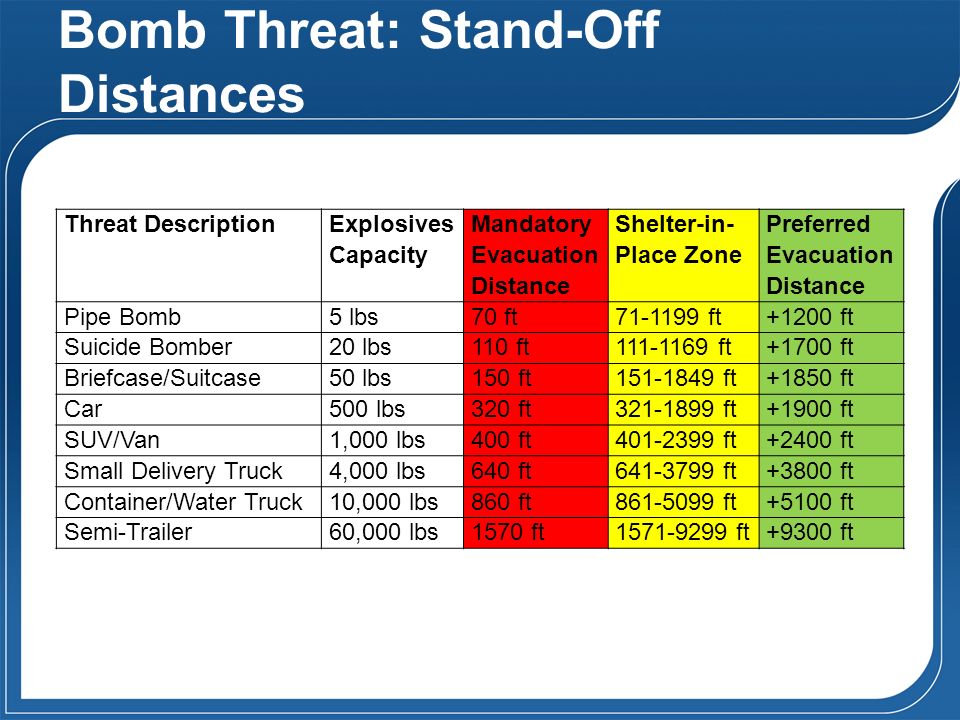
BOMB THREAT STANDOFF DISTANCES Pipe Bomb/Pressure Cooker Mandatory Evacuation distance 70 feet Preferred Evacuation distance 1,0 feet Severe injury/death PersonBorne IED Suicide Vest or Briefcase Mandatory Evacuation distance 110 feet Preferred Evacuation distance 1,700 feetNov 14, 16 · Explosives can be placed at a fixed distance from the workpiece After detonation the explosive forces travel through the intervening medium to reach the work piece This method is called the standoff method Alternatively, the explosive can be placed directly on the work piece Upon detonation, explosive forces hit the work piece directlyA *NOT* Vehicle Borne *NOT* Q Which of these is an example of an electric circuit?

Solved Assuming That The Building Is Subjected To An Expl Chegg Com
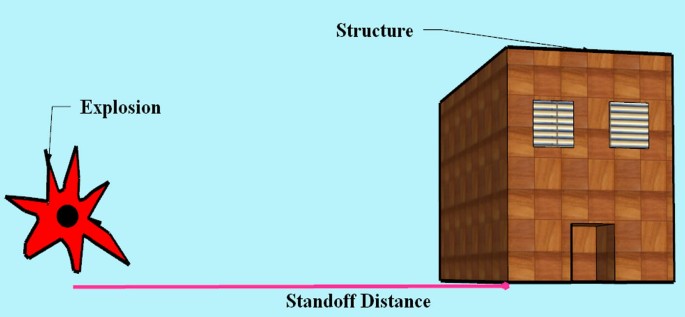
Stand off distance for explosives
Stand off distance for explosives-Standoff techniques have received increasing attention as valuable methods for material analysis at remote distances This is particularly relevant when looking at hazardous contaminants in the environment or residual explosive material, where it is desirable for the analyst to remain at a safe distance from the material being investigatedAt lesser standoff distances, even a small
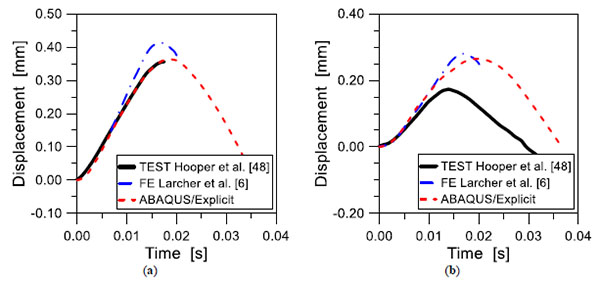



Passive Control Systems For The Blast Enhancement Of Glazing Curtain Walls Under Explosive Loads
However, the related issues of multiple target distances (from standoff to proximity) and sampling time scales (from passiveContents—Continued Criteria for NonDOD Explosives Activities (AE Operations and Storage) on US Army Garrisons or installations † 8–10, page 64 Subdivision of explosives quantities † 8–11, page 65 Interpolation and extrapolation † 8–12, page 65 Measuring distance † 8–13, page 65 Ammunition and explosives risk † 8–14, page 66 Blast considerations † 8–15, page 66Given for a range of standoff distances and explosive weight by the dimensionless scaled distance parameter Z=R/W^(1/3) Pertinent parameters are defined on the page 90 of Reference 52 TERM DEFINITION UNITS Pr peak positive reflected normal psi pressure
Detection of explosives, explosive precursors, or other threat agents presents a number of technological challenges for optical sensing methods Certainly detecting trace levels of threat agents against a complex background is chief among these challenges;Ideally, standoff detection occurs at a distance which provides the highest level of safety for the soldier or first responder These shorter wavelength methods have included primarily Raman based methods using visible (532 nm), near UV (355 nm), and deeper UV (262 nm, 248 nm, 224 nm, and 213 nm) excitationTriggers • What existing conditions are changing and are they Better or Worse
Dec 30, 17 · Q Which type of IED is used to deliver an explosive charge to a target with a large standoff distance between the firing point and the target?Mar 06, 12 · Standoff Distances Modifying a site begins with making the most of the existing standoff distance "Standoff distance is key," says David Dickinson, senior vice president with vehicle barrier manufacturer Delta Scientific "Standoff distances provide a clear space where no vehicles are permitted Every inch countsThese distances can be reduced for personnel wearing ballistic protection Note that the pipe bomb, suicide belt or vest, and briefcase or suitcase bomb are assumed to have a fragmentation characteristic that requires greater standoff distances than an equal amount of explosives in




Explosion Standoff Calculator




Explosives Detection Via Stand Off Raman Spectroscopy Investigation From A Safe Distance Zachhuber Bernhard Amazon Com Books
The cavity formed becomes deeper yet when the explosive charge containing the liner is removed some distance away from the plate There is an optimum standoff distance which varies with the liner and charge design Devices of this nature are called lined cavity charges or shaped chargesA shaped charge is an explosive charge shaped to focus the effect of the explosive's energy Different types of shaped charges are used for various purposes such as cutting and forming metal, initiating nuclear weapons, penetrating armor, or perforating wells in the oil and gas industry A typical modern shaped charge, with a metal liner on the charge cavity, can penetrate armor steelWhere Z is the ' scaled distance ' with units of m/kg 1/3, R is the distance (m) from the center of the explosive charge to the target, and W is the weight of the charge (kg);



A Critical Review Of Blast Wave Parameters And Approaches For Blast Load Mitigation Springerlink



Blast Load Predictions
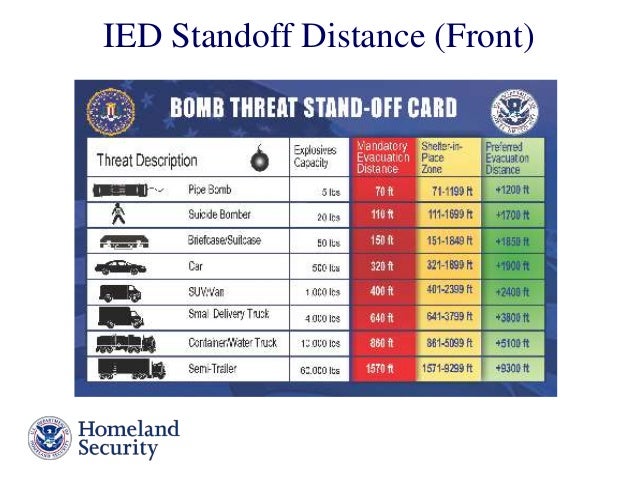
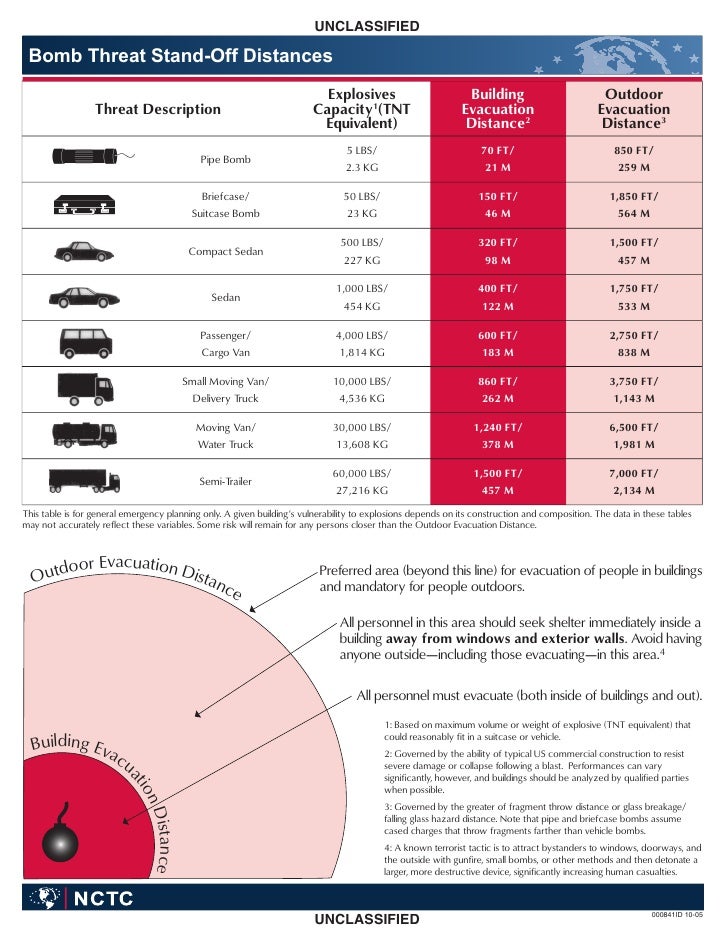
Standoff 15 feet YIELD ( TNT Equiv) ,000 lb Reflected PRESSURE 800 psi Standoff 80 feet 166 killed Comparison of Standoff Murrah Federal Building Khobar Towers 19 killedEXPLOSIVE BLAST 4 EXPLOSIVE BLAST 41 This chapter discusses blast effects, potential school damage, injuries, levels of protection, standoff distance, and predicting blast effects Specific blast design concerns and mitigation measures are discussed in Chapters 2 and 3 Explosive events have historically been a favorite tactic3 Governed by the greater of fragment throw distance or glass breakage/falling glass hazard distance Note that pipe and briefcase bombs assume cased charges that throw fragments farther than vehicle bombs 4 A known terrorist tactic is to attract bystanders to windows, doorways, and the outside with gunfire, small bombs, or other




Pdf Effect Of Stand Off Distance On The Mechanical And Metallurgical Properties Of Explosively Bonded 321 Austenitic Stainless Steel 1230 Aluminum Alloy Tubes Semantic Scholar



Securing Transportation Assets Operations Ppt Download
A Wires connected to a power source Q Which of these BEST defines an IED?Feb 09, 12 · UFC DoD Minimum Antiterrorism Standoff Distances for Buildings (FOUO), with Change 1 () Federal Facility Criteria Department of Defense Unified Facilities Criteria (UFC) Participating Agencies About WBDG WBDG is a gateway to uptodate information on integrated 'whole building' design techniques and technologies The goalDetermined by US firefighting practices wherein safe distances are approximately 4 times the flame height Note that an LPG tank filled with high explosives would require a significantly greater standoff distance than if it were filled with




Jcat Counterterrorism Guide For Public Safety Personnel




Chapter 3
Abstract We report THz sensing of explosive materials placed up to 30 m away from the emitter The absorption peak of RDX at 0 THz is measured using THz time domain spectroscopy (THzTDS) Experimental results support the possibility of applying THz wave technology for remote sensing and detection of explosives and related compounds at long standoff distancesW is usually the TNTequivalent weight This scaling law indicates that two charges with similar geometry in the same ambient conditions, identical explosive composition, and different size (weight) will produce selfRaman spectra of a sample to detect the presence of explosives in trace quantities, at a standoff distance Partial least squaresDiscriminant analysis (PLSDA) was used to identify peaks in the Raman spectra of the sample, which could better differentiate explosive and nonexplosive




Passive Control Systems For The Blast Enhancement Of Glazing Curtain Walls Under Explosive Loads




Stand Off Distance An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
The standoff distance, which is an independent variable like V D, is selected to achieve a specific dynamic bend angle and velocity of impact The dynamic bend angle is a dependent variable that is controlled by the detonation velocity (V D) and the standoff distance Typical values for y are between 2 and 25 degreesStandoff • Inside a controlled perimeter or not • If Within a controlled perimeter is it within 0' of it (Explosive Weights I & II) • How is the site configured with Parking, Roadways, markings, etc?Standoff distance 10m T amb = 22 oC RH = 14% V wind = 10 mph Field Testing at Yuma Proving Ground IR image TNT detected at 10 meter standoff 3 inch explosives in a stand off configuration • RED concept has been demonstrated on variety of substrates, analytes, in/out doors, and at significant




Normalized Time T O T O T In Function Of The Stand Off Distance R Download Scientific Diagram




Stand Off Distance An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Jul 08, 16 · Information on explosives directs users to Guide 112 (orangebordered pages) for all explosives except for explosives 14 (explosives C) and explosivesThe distance of the protected building from the point of explosive detonation is commonly referred to as the standoff distance The critical locations for detonation are taken to be at the closest point that a vehicle can approach, assuming that all security measures are in placeQuickly define safe standoff distances around the location of a potential explosives threat Calculate rough damage and injury contours Suggest appropriate roadblocks Identify other nearby facilities of concern (eg, schools, hospitals, and care centers)




Solved Assuming That The Building Is Subjected To An Expl Chegg Com




Detecting Explosives At A Distance With Light Tech Pulse Sep 08 Photonics Spectra
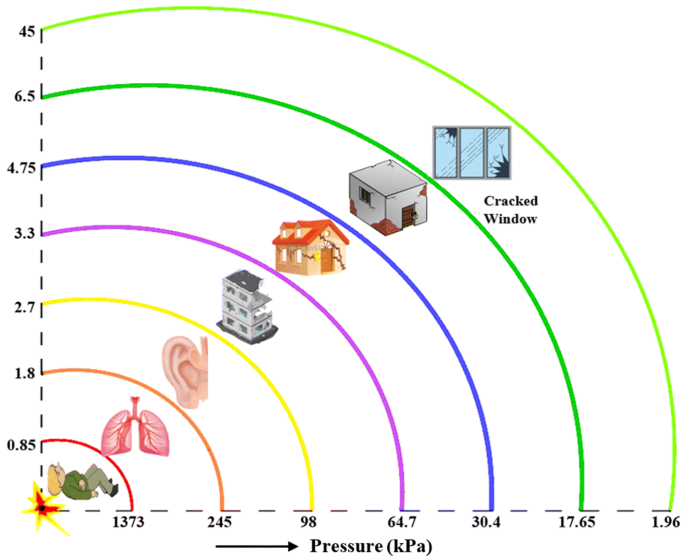
Class 1 Explosives Division 1 1 Explosives which have a mass explosion hazard Division 1 2 Explosives which have a projection hazard but not a mass explosion hazard Division 1 3 Explosives which have a fire hazard and either a minor blast hazard or a minor projection hazard or both, but not a mass explosion hazardJan , 17 · Scaled Distance is a commonly used technique for estimating the vibration and air overpressure from blasts The term scaled distance is given because the blast where the weight fired per 8ms delay is scaled to one pound of dynamite For example, in this video Anthony Konya explains that if 25 pounds of explosive is detonated, the estimatedThe smallest standoff distances, about 70 feet from the threat, are used for small pipe bombs with about five pounds of explosives A human suicide bomber with about pounds of explosives strapped to his/her body has a standoff distance of 110 feet A briefcase or suitcase bomb with about 50 pounds of explosives has a 150 foot standoff distance




Figure 1 Resonance Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy On Explosives Vapor At Standoff Distances




Explosives Detection Via Stand Off Raman Spectroscopy Investigation From A Safe Distance Zachhuber Bernhard Amazon Com Books
Ness and continuity At detonation, the focusing of the explosive high pressure wave as it becomes incident to the side wall causes the metal liner of the LSC to collapse–creating the cutting force If the standoff distance is optimum, collapse of the liner will be complete before itIncluding protection through design and understanding of blast engineering and safe standoff distances The identification of key threats is the first stage of any blast study for a new development Explosion threat scenarios are typically specified in terms of an explosive charge weight at a standoff distance from the target structureNov 01, 18 · standoff distances for facilities located close to explosive storage areas This approach works well for large quantities of explosives at large ranges, when the loading duration approaches that of a quasistatic load Originally, ATFP practice incorporated scaled range standoff distances due to the limited testing data available then




Contours Of The Critical Stand Off Distance In Metres As Function Of Download Scientific Diagram




Incident Pressure Produced By A 90 Kg Charge Of Anfo Explosive At A Download Scientific Diagram
Users construct an evaluation scenario by defining the potential explosion site (PES) type, the net explosive quantity (NEQ) and Hazard Divisions (HDs) being stored within the PES, identify nearby exposed sites (ES) and their distance from the PES, ES occupancy, and ES replacement cost The tool assesses the PESES scenario and provides aStandoff Detection Current methods of screening vehicles for explosive threats primarily rely upon what the agents can see during physical inspections These approaches have proven both time consuming and expensive To improve the ability to screen for threats within a vehicle at federal buildings or at large public events, S&T is developingUsually, the standoff distance available and the assumed size of the explosive device will determine the blastresistant features that must be provided Large explosive devices detonated at relatively great standoff distances will produce a large but uniform pressure over the surface of the building;




Advances In Standoff Detection Make The World Safer Features Apr 13 Photonics Spectra




Shaped Charge Wikipedia
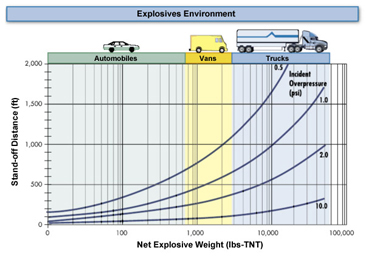
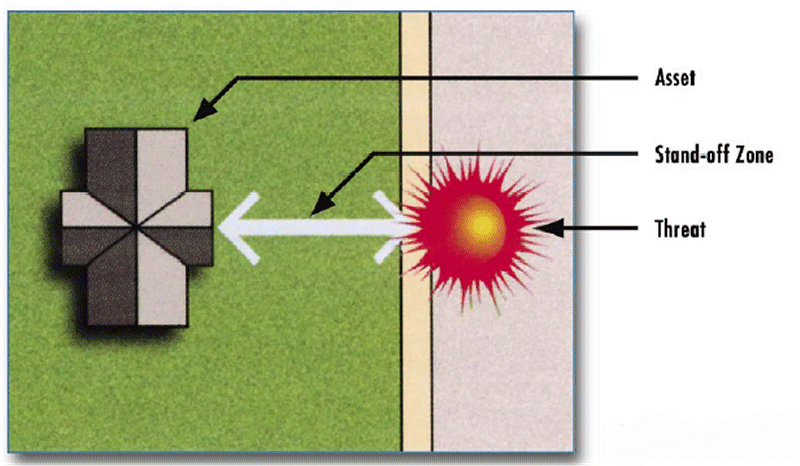
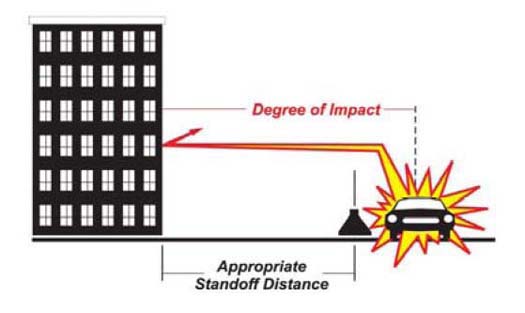
Nov 02, · Blast standoff (the distance between the explosive and the asset) is the single most important factor in determining the extent of damage that can be caused This isBomb Threat StandOff Distance Chart Print;Explosives are generally within the financial and technical capabilities of terrorists – IEDs can be assembled with relative ease and used remotely Terrorist groups of concern to Australia, the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), AlQa'ida, and supporters of these groups, have conducted explosives based attacks throughout the world




Optical Standoff Detection Eliminating Threats At A Distance Optics Photonics News




Explosion Welding Keith Powell Michael Fernandez Staton Burrell
Threat descriptions, explosive capacities, building evacuation distances, and outdoor evacuation distances Click here to download Published in NCTC Resources back to top Related Documents Intelligence ReformStandoff Distance 37 The standoff distance is the maintained distance between where a vehicle bomb is allowed and the target The initial goal should be to make that distance as far from theImprovised Explosive Device (IED) Safe Standoff Distance Cheat Sheet open pdf 168KB This document is a cheat sheet for the specific threat posed by improvised explosive devices The sheet gives an estimate of how far a person should stand from different explosive devices to avoid any injury United States Department of the Army




Nemesis Counter Ied Standoff Detection Of Buried Concealed Ieds
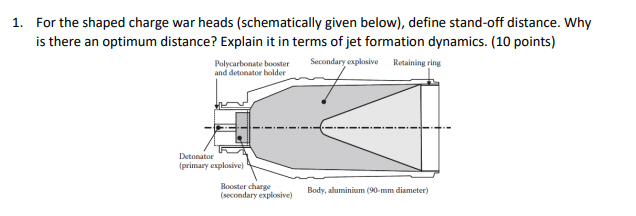



1 For The Shaped Charge War Heads Schematically Chegg Com
Jun 01, · In open explosions, the scaled distance "Z" is used to reflect the relationship among explosive equivalent, standoff distance and pressure, obtained by dimensional analysis and experimental data , , The equation for the scaled distance is (5) Z = R W 3 (6) Z = R ρ V 3 = 1 ρ 3 R V 3 where R is the standoff distance and W is explosion




Pdf Deep Ultraviolet Standoff Photoacoustic Spectroscopy Of Trace Explosives Semantic Scholar



Offshc Gets Briefed On Ieds




Improvised Explosive Device Ied Safe Stand Off Distance Emergency Response Guidebook 16 Canut Emergency Response Improvised Explosive Device Guide Book




Chapter 3



Bomb Stand Off Chart




Seds




Explosive Welding Of Metals Part One Total Materia Article




Ce Center Design To Protect




Figure 1 Resonance Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy On Explosives Vapor At Standoff Distances



Bomb Threat An App For That Too Homeland Security
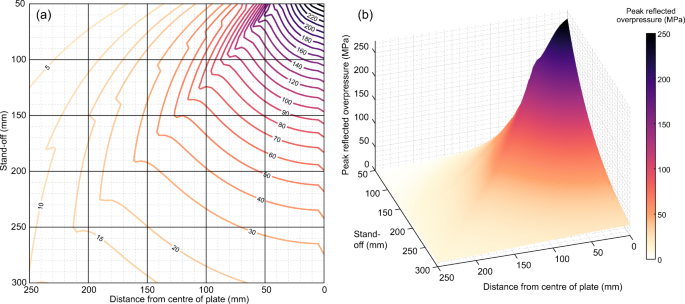



Reflected Near Field Blast Pressure Measurements Using High Speed Video Springerlink




Jcat Counterterrorism Guide For Public Safety Personnel
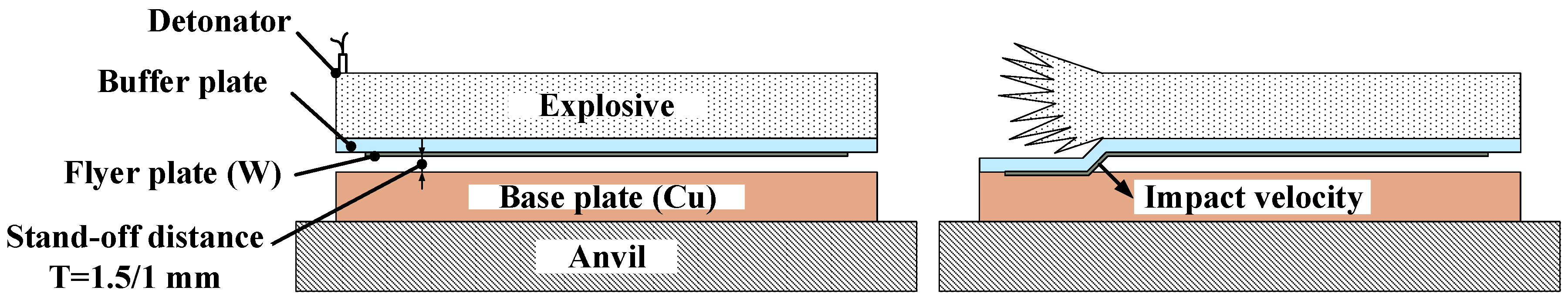



Materials Free Full Text Numerical And Experimental Studies On The Explosive Welding Of Tungsten Foil To Copper Html




Critical Charge Weight Standoff Distance For No Damage For Medium Spall Download Scientific Diagram




Explosive Forming An Overview Metalwebnews Com



Govspeak Standoff Government Solutions




Explosion Welding Principle Working Types Application Advantages And Disadvantages Mech4study




Pdf Standoff Detection Of Explosive Substances At Distances Of Up To 150m




Detecting Explosives At A Distance With Light Tech Pulse Sep 08 Photonics Spectra




An Explosive Ordnance Disposal Truck Stands On A Range During Standoff Munitions Disruption Training July 28 Aboard Camp Schwab Okinawa Japan The Training Ensured Explosive Ordnance Disposal Technicians Were Proficient In The




Standoff 0 Standoff Handheld Chem Bio Explosives Analyzer Photon Systems




The First Responder
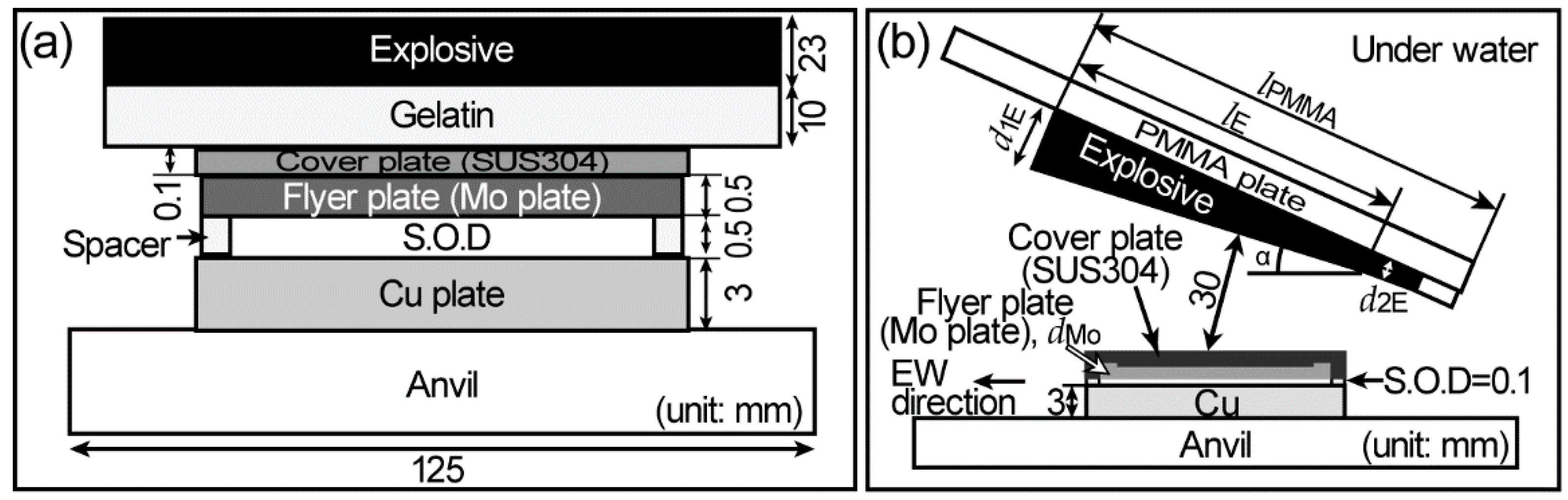



Metals Free Full Text Characterization Of Shock Wave Damages In Explosion Welded Mo Cu Clads Html




Explosives And Ied Detection Portable Reliable Detection




Blast Resistant Design Of Structures Practice Periodical On Structural Design And Construction Vol 19 No 2




The First Responder




Explosive And Blastwall Simulation Using Ls Dyna Skill Lync
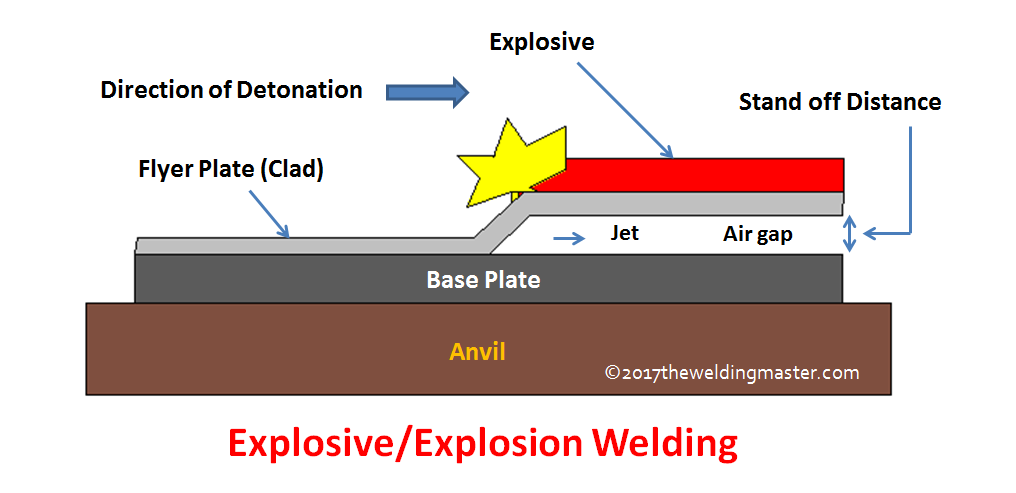



Explosive Welding Equipment Types Working Advantages And Disadvantages With Application The Welding Master




An Overview Of Antiterrorismforce Protection Understanding Application And




Simulation And Experimental Investigation Of Jetting Penetrator Charge At Large Stand Off Distance Sciencedirect




Stand Off Hyperspectral Raman Imaging And Random Decision Forest Classification A Potent Duo For The Fast Remote Identification Of Explosives Analytical Chemistry X Mol




Explosive Potential Electro Optics



A Critical Review Of Blast Wave Parameters And Approaches For Blast Load Mitigation Springerlink




Review Of Explosive Detection Methodologies And The Emergence Of Standoff Deep Uv Resonance Raman Gares 16 Journal Of Raman Spectroscopy Wiley Online Library




Dhs Bomb Threat Stand Off Chart Public Intelligence




Jcat Counterterrorism Guide For Public Safety Personnel




Drdo S New Bomb Detection Device Can Spot Homemade Explosives From Two Meters Away Business Insider India




Stand Off Raman Spectroscopy A Powerful Technique For Qualitative And Quantitative Analysis Of Inorganic And Organic Compounds Including Explosives Springerlink




Microstructure And Mechanical Properties Of Ti Cu Clads Manufactured By Explosive Bonding At Different Stand Off Distances Scientific Net




Dave Andrew Counter Improvised Explosive Device Instructor Marine Corps Engineer School Teaches Itx For Spouses Participants How To Use A Holley Stick At Range 800 Aboard Marine Corps Air Ground Combat Center




Fmi 3 07 22 Appendix C Population And Resources Control




Bomb Threat Stand Off Chart This Chart Offers Information About How Download Scientific Diagram




Standoff Detectors For Cbe Photon Systems



Transit Security Design Considerations




Explosives Detection Via Stand Off Raman Spectroscopy 978 3 81 3259 4 By Bernhard Zachhuber




Experimental Determination Of Acceleration Of Explosively Driven Metal By Photonic Doppler Velocimetry In The Process Of Explosive Welding Kucera 18 Propellants Explosives Pyrotechnics Wiley Online Library




Investigation Of Effect Of The Stand Off Distance On Interface Characteristics Of Explosively Welded Copper And Stainless Steel Sciencedirect




Standoff Detection And Imaging Of Explosives Using Cars Semantic Scholar




Atf Vehicle Bomb Tables




You Have Been Tasked With Evaluating An Existing O Chegg Com




An Overview Of Methods For Blast Load Testing And Devices For Pressure Measurement
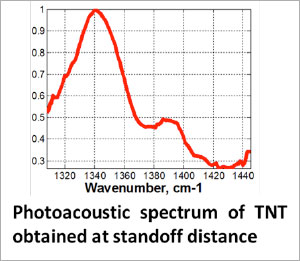



National Center For Physical Acoustics Standoff Photoacoustic Detection Of Solid Residue Of Explosives And Other Chemicals




Ied Guide




Predicted Blast Parameters Of Panels With Respect To Tnt Explosive Download Table



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿